[first, last] = input["What is your name",[["First
Name", "Jeff"], ["Last Name", "Albertson"]]]
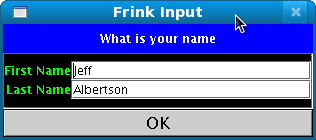
This works on Swing, AWT, and Android GUIs, and in pure text mode.
b = new set[1,2,3] // Construct a set with
the specified elements
toSet[x] function to turn the specified
expression into a set, if possible. This works with enumerating
expressions, arrays, or simple expressions (making a single-item set out of
the latter.)
c = [3,6,9]
// Create an array
d = toSet[c] // Create a set from the
array
The following single-line program demonstrates turning an enumerating
expression into a set (the lines[url] function returns
an enumerating expression of all of the lines in a file,) turning that into
an set (to remove duplicates) and sorting it (implicitly turning it into an
array in the process.) The result is a sorted array containing all of the
unique lines in a file, discarding duplicates.
sort[toSet[lines["file:myfile.txt"]]]
#!/path/to/frink
then you can start Frink programs easily from a (newish) Bourne or bash
shell, by just typing the filename, instead of frink
thefilename. (Up until recently, many versions of bash or sh
wouldn't allow you to specify another script as your start script; it
required an "executable binary" magic number.)